Keep Your Secrets Secret

Morgan Holm
Nov 15, 2023

Compromised secrets are an attack vector that is being seen more frequently in breaches. Since many secrets provide unrestricted access to data stores or have elevated privileges, they can have devastating consequences. R&D teams need to handle many secrets, especially for hybrid and cloud environments development. They are often doing this outside of the purview and guidance of security teams. This leads to a lack of control over where and how the secrets are being used and shared, greatly increasing the risk of a breach.
What are Secrets?
Secrets in cybersecurity refer to digital authentication credentials. There are a variety of types of secrets that include user passwords, encryption keys, API keys, application keys, and certificates among others.
These secrets serve a variety of purposes, from securing data at rest or in transit to granting access to important computing resources and data.
While usernames and passwords are a common example, there are several ways to help protect and elevate their security. Non-human secrets are equally if not more important but are often overlooked. They are also far more challenging to secure and protect. For this post we are going to focus on the non-human secrets.
The proliferation of modern applications, whether hybrid, on-premises or in the cloud, has increased the importance of managing different types of digital secrets, especially in the context of application-to-application interactions.
Secrets management plays a key role in ensuring consistent and secure application of these credentials across the enterprise. Many organizations put policies in place that all non-human secrets must use their secrets management systems.
We have Secrets Management so we’re all good, right?
Secrets management solutions are required to maintain a secured repository with strict access controls to keep them safe. They may even help how they are transmitted, shared and how frequently they get rotated. How do you ensure that your secret management system(s) are being used. You need to look at the complete secrets lifecycle to be sure your policies are being followed. Secrets scanning or discovery is a process that looks through the technology stack, code repositories, CI/CD pipelines, and libraries and potentially even your collaboration tools to find where secrets could be exposed such as hardcoded plain text secrets or ones that match a known pattern. Various solutions may be very good at finding exposed secrets but still may miss some. Code repositories like GitHub will point them out and some DevSecOps tools will also help prevent accidental publishing of secrets. Instead of trying to find every secret wouldn’t it be nice to know when one is created outside of your secrets management solution?
In the following example we will show how Cygna Auditor allows you to see these events in a report and create a real-time alert that will proactively notify you when a secret is created outside of the secrets management system.
AWS Events
When a secret is created in AWS Secrets Manager the following event is created in Cygna Auditor for AWS.
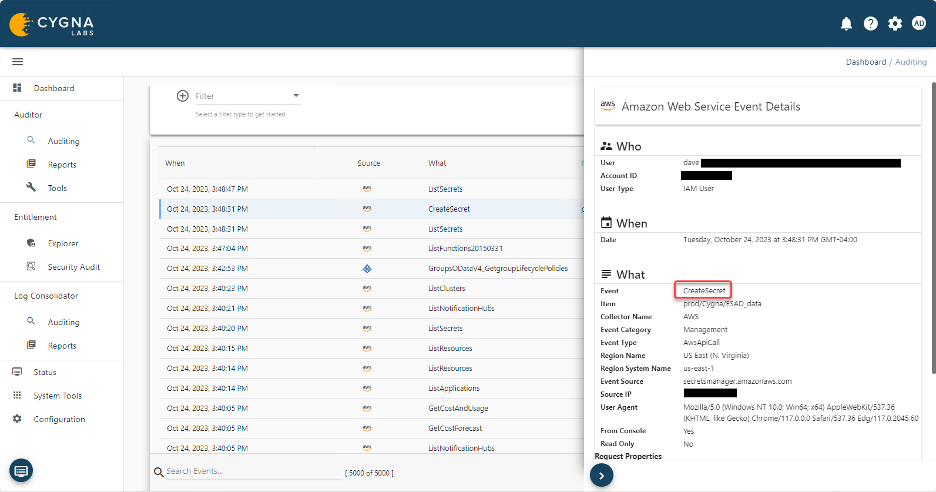
When someone creates an access key on an identity, the event would be like the following.
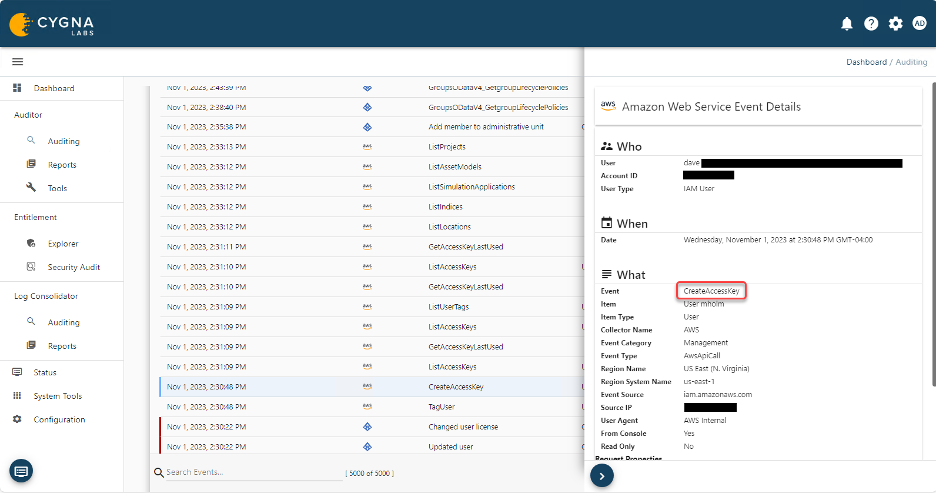
Since this secret was not created in the AWS Secrets Manager per policy, you can have a report and or a real-time alert sent to the security team to investigate further.
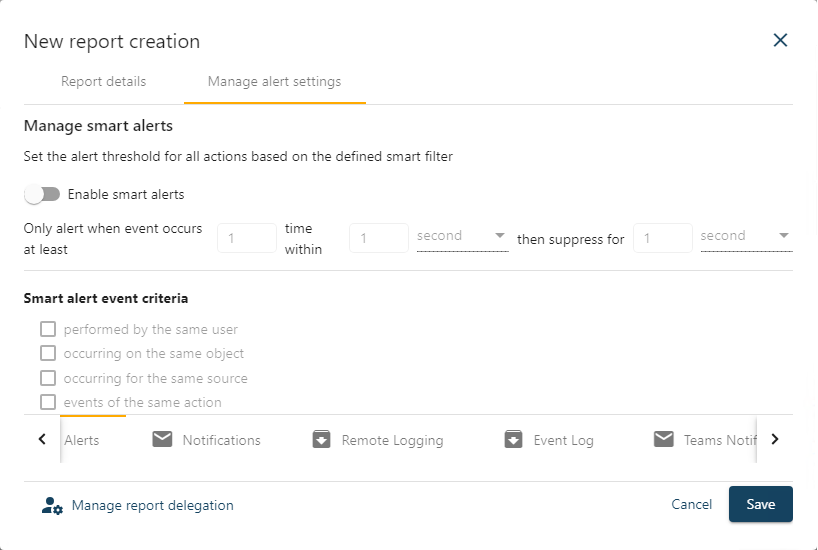
This allows you to see a secret when it’s created and to be notified if it’s against your security policy. Monitoring secrets isn’t just something you do when they are created but you also need to watch what activities are being done with them, especially if they have elevated privileges. Detect and monitor secrets creation and usage in your environment to minimize your security risk.